Manage developers
Overview
In SEI 2.0, developers are the most fundamental unit of measurement. Every insight, metric, and analysis in SEI ultimately ties back to developers i.e. the people contributing to your code, issues, and deployments. Managing developer records ensures that every individual in your organization is accurately represented in SEI, mapped to the right teams, roles, and organization structures.
You can manage developer data in SEI 2.0 in two ways:
- Via CSV Upload: Recommended for initial setup using an HRIS export that aligns with SEI’s schema.
- Via Developer CRUD APIs: Recommended for ongoing programmatic updates or synchronization with your internal systems.
Both approaches support the same data schema and enable complete lifecycle management of your developer records.
Who is a developer
A developer in SEI 2.0 represents an individual whose work or contributions are analyzed in SEI dashboards. Developers are created through:
- CSV uploads from HRIS or internal systems, or
- Programmatic inputs via SEI’s Developer APIs.
Once added, SEI automatically correlates each developer’s data across source systems like GitHub, GitLab, Jira, or Azure DevOps. The Developers page in SEI includes:
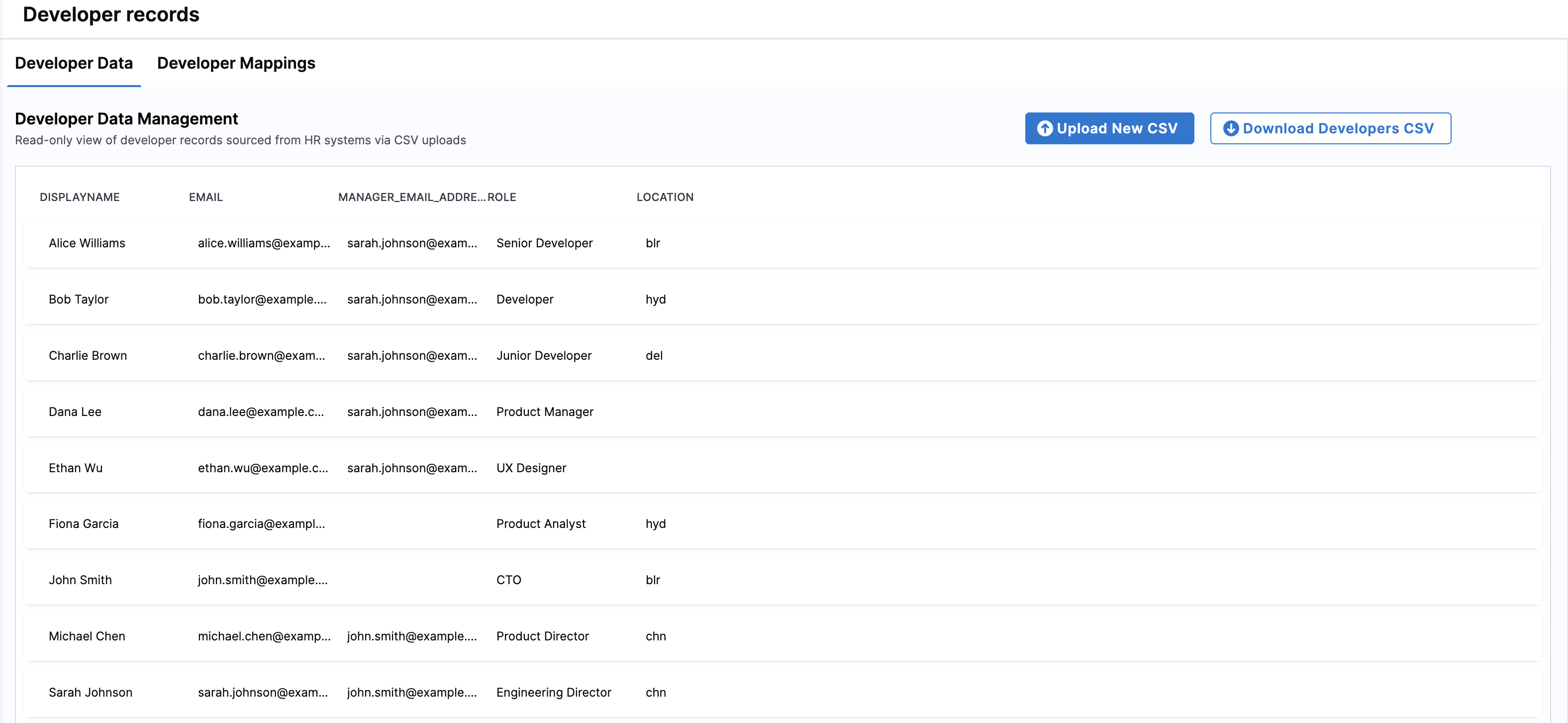
- Developer Data tab: A read-only view of ingested developer records (from CSVs or APIs).
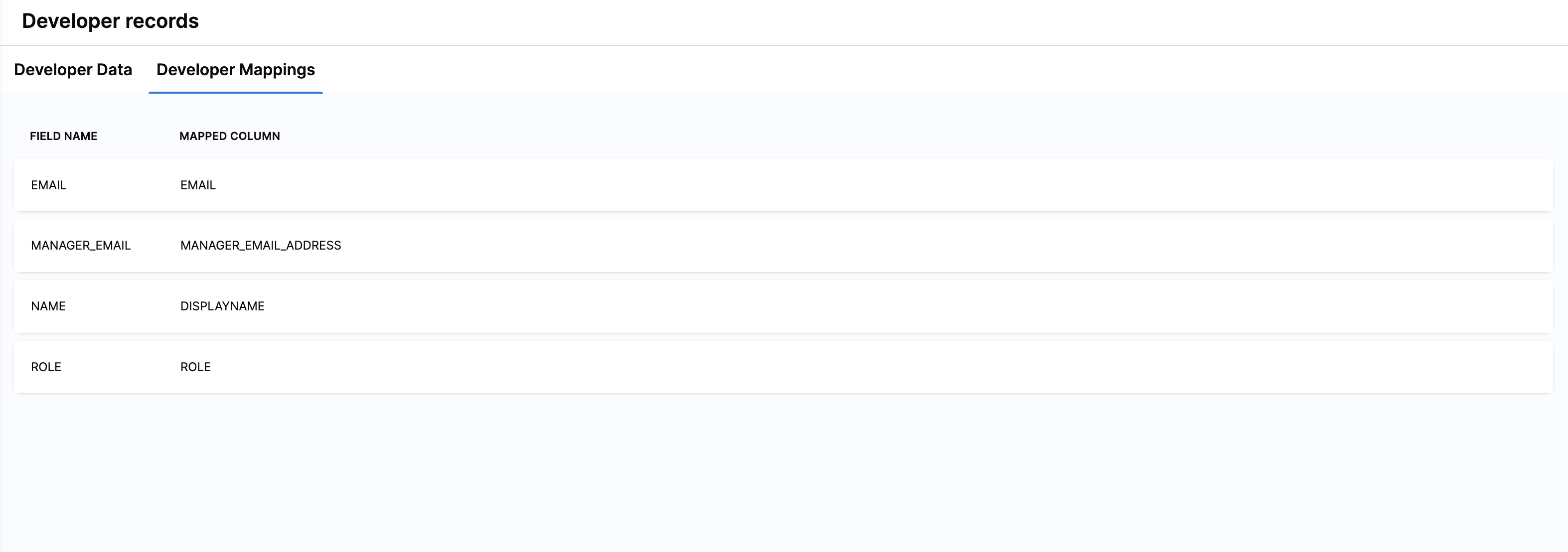
- Developer Mappings tab: A configuration interface that maps raw input fields (like email or manager email) to SEI-specific schema fields (EMAIL, MANAGER_EMAIL, DISPLAYNAME, ROLE, etc.). This mapping ensures SEI correctly interprets your organization’s developer records and establishes relationships between individuals, teams, and managers.
What is a developer identity
Each developer in SEI is linked to identities discovered across different integrated systems — such as GitHub, Jira, or Bitbucket. These identities could be:
- Usernames (e.g., @johndoe)
- Account IDs, or
- Emails used within each source system.
SEI automatically identifies and correlates these identities using the Auto Identity Discovery Engine i.e. a system that connects contribution data to developers through email-based correlation.
Always ensure that the email address used in SEI matches the email your developers use across source systems. Incorrect or mismatched emails may result in missing or fragmented identity mappings in SEI.
Preparing the developer records
Before uploading your developer records into SEI, ensure your source data (CSV or system of record) meets the following standards.
| Requirement | Description |
|---|---|
| Managers must also exist as developers | Every email listed as a Manager Email must also appear as a separate developer record. This ensures SEI can construct an accurate reporting hierarchy. |
| No cyclic relationships | Avoid circular manager-reportee chains (e.g., A → B → A). These relationships will break hierarchy creation. |
| Unique developer emails | Each developer record must have a unique email address. Duplicate emails will cause ingestion errors or incorrect identity attribution. |
| Required fields | Each record must include at least the following fields: Name, Email, and Manager Email. You may also include additional fields used for org tree filters / configurations. |
| No missing values | Ensure Name and Email are populated for every record. Missing values will cause failure. |
| Email correctness | Use the same email IDs that developers use across your source systems (GitHub, Jira, etc.). A mismatch will prevent SEI from linking identities correctly. |
| No blank column names | Every column in your CSV should have a valid header. Blank column headers will cause validation errors. |
Add developer records via CSV upload
The CSV upload method is ideal for initial setup or periodic manual updates.
To upload developer records:
-
In your SEI 2.0 environment, go to Configuration > Developers from the left-hand navigation pane.
-
Click Upload New CSV to add a new developer dataset.
-
Browse and select your CSV file containing developer data.
-
Review the Developer Preview screen. Map each column from your CSV to the corresponding SEI field.
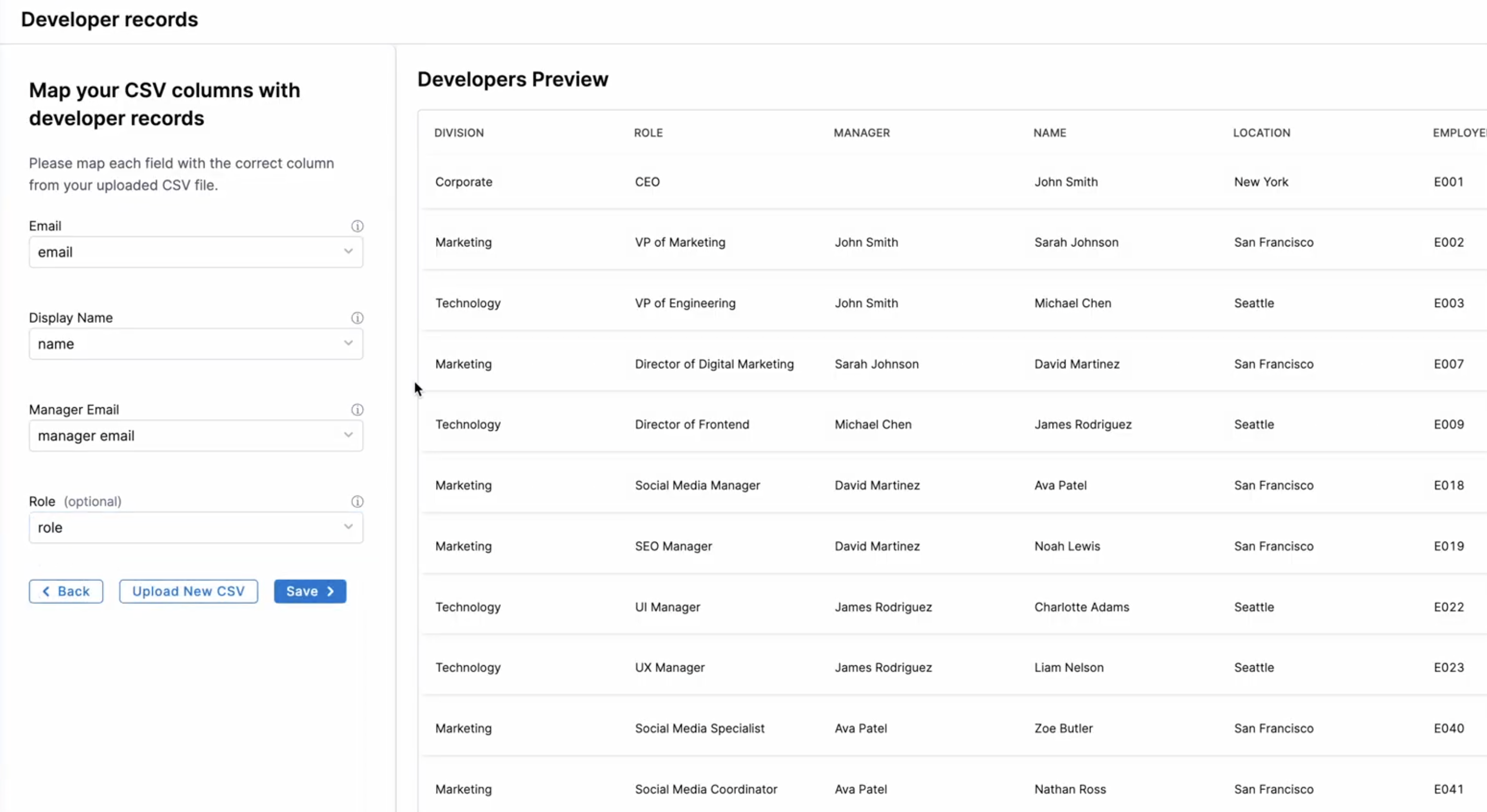
- Display Name: Select the column containing the developer's name.
- Email: Select the column containing the developer's email.
- Manager Email: Select the column containing the manager's email.
- Role: Optionally, select the column containing the developer's role.
-
Click Save. A success message "Developer records saved successfully" will confirm that the upload was processed.
After upload, validate your hierarchy by checking the Developer Data and Developer Mappings tabs to ensure all records were processed correctly.
Add developer records via Developer CRUD APIs
For automated or large-scale synchronization, you can manage developer records programmatically using the Developer CRUD APIs. These APIs allow you to create, update, delete, or retrieve developer data as part of your integration or HRIS sync workflow.
| Operation | Method & Endpoint | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Upsert developers | PATCH /v2/developers | Add & update developer records in bulk. |
| Delete developers | DELETE /v2/developers | Remove developer records from SEI. |
| Get developer schema | GET /v2/developers/schema | Retrieve the schema definition for developer records. |
| Download developer data | GET /v2/developers/download | Download all developer records from SEI. |
Note: These APIs are ideal for syncing SEI with your HRIS or internal employee directory, ensuring your developer data remains up to date without manual uploads. For detailed request and response formats, refer to Using CRUD APIs to update developer records.
Managing developer records
Accurate mappings are essential for ensuring developer records are correctly associated with roles, managers, and team assignments. Field mappings are available on the Developer Mappings tab. You can access these mappings to ensure that the fields from the uploaded CSV file are correctly mapped to SEI's schema.
To review or export existing developer data:
- Navigate to the Developer Data tab to view all developer records in SEI 2.0.
- Click Download Developers CSV to export the data. This provides a snapshot of the current records in CSV format for auditing or offline review.
